Features:
OIML Class:M1/F2
Adjustment:External Calibration
The Calibration device for weight comparators has been granted a Utility Model Patent.
The automatic lifting and arrestment device for weight comparators has been granted a Utility Model Patent.
High precision, quick response, accurate and reliable, easy operation
Applications:
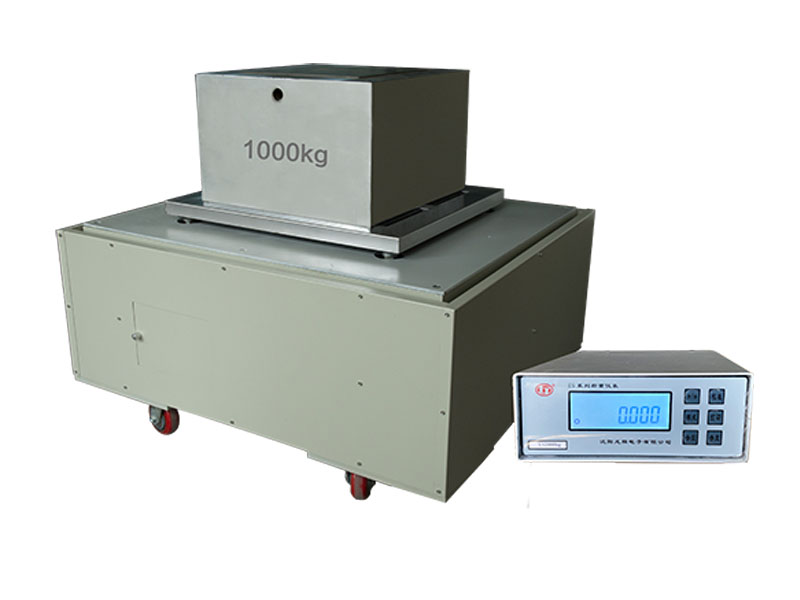
Weight Comparators find extensive application in industrial metrology and metrological verification of M1 weights.
It is particularly employed for quantitative measurement.
Specifications:
|
Model |
Capacity |
Readability |
Repeatability |
Pan Size |
EXT Dimension |
|
ES-500F2 |
500 kg |
1 g |
±1 g |
1200 ×1000 mm |
460×205×280 mm |
|
ES-1000F2 |
1000 kg |
1 g |
±1 g |
||
|
ES-1000M1 |
1000 kg |
5 g |
±5 g |
||
|
ES-2000M1S |
1000 kg |
5 g |
±5 g |
||
|
2000 kg |
10 g |
±10 g |
FAQs
1.What is a mass comparator?
A mass comparator, or mass comparator balance, is a gravimetrical measuring instrument with high resolution and exceptional repeatability, enabling the smallest difference in mass to be accurately determined. Window-range mass comparators offer high resolution weighing in a 'window' around a defined weight value and are used purely for mass calibration and mass determination for masses within this window. However, full-range mass comparators are highly versatile and can be used not only for weight determination but also for general weighing applications, particularly those in which there are small samples and large tare loads or when large and small sample qualities need to be combined in one weighing process.
2.What is the difference between weighing and mass comparison?
In a regular weighing process, the balance is calibrated and the weight result of any item placed on the balance is measured from zero g.
This process is called "absolute weighing".
Mass comparison, which is used for weight calibration, is a specific type of differential weighing in which the reference point is not the calibrated balance but is the reference weight against which the test weight is compared.
Hence why this type of balance is known as a mass comparator.
When calibrating a test weight, the reference weight to which it is compared must be at least one accuracy class higher than the test weight.
However, the reference weight must also be calibrated against another weight in an even higher accuracy class.
This chain of comparisons provides metrological traceability to the definition of the kilogram based on Planck's constant.
3.What is the difference between a mass comparator and a balance?
A mass comparator and an balance have the same design and work according to the same principles.
The difference between a mass comparator and a balance is the performance, in particular the readability and repeatability.
Regular laboratory balances are specified by the main performance properties: repeatability (RP), eccentricity (EC), nonlinearity (NL) and sensitivity (SE).
However, as weight calibration is carried out by differential weighing, mass comparators are additionally specified with differential weighing repeatability ABA (RP ABA).